Female Sexual Disorders Explained: From Vaginismus to Anorgasmia — and How Yoni Therapy Can Help
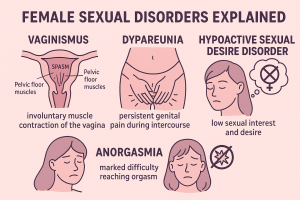
Female sexual dysfunction is complex, multifactorial, and under-discussed — yet it affects nearly 40% of women at some point in their lives. This guide offers a medically accurate, complete overview of the most common sexual disorders affecting women, their causes, symptoms, and how integrative practices like yoni therapy can support healing.
Yoni therapy, while rooted in ancient traditions, is increasingly recognized as a somatic and trauma-informed approach that complements medical care in addressing sexual pain, arousal challenges, and emotional disconnection.
Understanding Female Sexual Disorders
Sexual dysfunction in women can be classified by one or more of the following domains:
- Desire
- Arousal
- Orgasm
- Pain
- Emotional or relational distress
Disorders can be primary (lifelong), secondary (acquired), situational, or generalized. They may be caused by physical conditions, trauma, hormonal imbalances, neurological dysfunction, or psychosocial factors.
1. Vaginismus
An involuntary contraction of the pelvic floor muscles surrounding the vaginal canal, making penetration painful or impossible.
- Symptoms: Burning, stinging, tightness, automatic clenching when penetration is attempted.
- Causes: Trauma, fear, religious conditioning, past abuse, or lack of education.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Re-education of the pelvic floor, breathwork, manual internal release, and emotional reframing help reduce reflexive guarding.
2. Dyspareunia
Painful intercourse. Can be superficial or deep, with physical, hormonal, or psychological origins.
- Symptoms: Sharp, burning, stabbing, or aching pain during or after sex.
- Common Causes: Endometriosis, infections, hormonal thinning, pelvic scarring.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Tissue desensitization, scar release, fascia work, and nervous system regulation.
3. Anorgasmia
Persistent inability to reach orgasm despite adequate stimulation.
- Types: Primary (never orgasmed) vs. secondary (used to orgasm).
- Contributors: Shame, lack of clitoral stimulation, medications (SSRIs), trauma.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Mapping pleasure, restoring safety, increasing clitoral awareness, and deconstructing orgasm performance pressure.
4. Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder (HSDD)
Marked absence of sexual thoughts, fantasies, or desire — causing personal or relational distress.
- Factors: Stress, hormonal imbalance (low testosterone, high cortisol), poor body image, unresolved relationship issues.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Energetic connection, touch reawakening, identifying erotic blueprints, and healing subconscious aversion patterns.
5. Sexual Arousal Disorder
Inability to attain or maintain sexual arousal despite adequate desire.
- Mechanism: Disconnection between mental interest and genital response.
- Causes: Blood flow issues, nerve damage, anxiety, SSRIs.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Stimulating blood flow, rebuilding sensory pathways, and addressing emotional resistance.
6. Vulvodynia
Chronic pain or discomfort at the vulva with no clear identifiable cause.
- Pain Types: Generalized, provoked, spontaneous, or localized.
- Possible Causes: Nerve injury, inflammation, hormonal sensitivity.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Gentle touch desensitization, breath-coordinated internal mapping, trauma release.
7. Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder (GPPPD)
DSM-5 diagnosis that merges vaginismus and dyspareunia. Includes fear, tension, and pain with penetration.
- Multifactorial: Involves physical, psychological, and relational elements.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Whole-person approach: somatic work, education, and therapeutic dialogue.
8. Clitoral Hypoesthesia
Reduced or absent clitoral sensation.
- Causes: Nerve trauma, genital cutting, chronic tight pelvic floor, neurological disorders.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Sensate focus techniques, myofascial release, and clitoral mapping.
9. Persistent Genital Arousal Disorder (PGAD)
Unwanted, persistent genital arousal unlinked to desire or sexual stimulation.
- Distressful: Often debilitating and misunderstood.
- Etiology: Pudendal nerve dysfunction, cysts, withdrawal from antidepressants.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Nervous system downregulation, grounding touch, and trauma-informed care.
10. Female Sexual Interest/Arousal Disorder (FSIAD)
Combined diagnosis in DSM-5 involving both low desire and arousal.
- Prevalence: Most common female sexual dysfunction.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Revitalizing sensual connection, addressing body memory blocks, co-regulation practices.
11. Vestibulodynia
Pain at the vaginal entrance (vestibule), often triggered by touch or pressure.
- Signs: Burning, stabbing, rawness when touched.
- Causes: Hormonal birth control, yeast overgrowth, nerve hypersensitivity.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Touch tolerance re-education, low-pressure manual therapy, neuroplasticity-based retraining.
12. Post-Coital Dysphoria (PCD)
Sadness, anxiety, or irritability following consensual sex.
- Reasons: Hormonal drop (oxytocin, prolactin), trauma reactivation, shame response.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Emotional integration, aftercare techniques, and self-compassion work.
13. Sexual Aversion Disorder
Extreme aversion to sexual contact causing distress or avoidance.
- Related to: PTSD, religious trauma, assault history.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Consent-based bodywork, titration of touch, and safety restoration through breath and somatic awareness.
14. Female Orgasmic Disorder
Delayed, infrequent, or absent orgasms — despite arousal and desire.
- Common Factors: Medication, shame, lack of clitoral focus, relational disconnection.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Deprogramming sexual scripts, clitoral anatomy education, and embodied pleasure training.
15. Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
Tight, weak, or uncoordinated pelvic muscles affecting arousal, pain, or orgasm.
- Symptoms: Pain during sex, incomplete bladder emptying, low tone or spasm.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Internal release, breath-pelvis coordination, restoring muscular awareness.
16. Lichen Sclerosus
Chronic inflammatory skin condition affecting vulvar tissue.
- Effects: Thinning, white patches, tearing, scarring.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Supportive touch, pain-reducing breath, and collaboration with dermatological care.
17. Endometriosis-Related Dyspareunia
Painful sex due to lesions, scarring, or inflammation from endometriosis.
- Impact: Deep pelvic pain, relational anxiety.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Scar release, pelvic unwinding, inflammation-calming techniques.
18. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Infection-induced inflammation of reproductive organs.
- Consequences: Pain, adhesions, long-term fertility issues.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Post-infection healing, tissue mobilization, internal de-armoring.
19. Labial Adhesions
Labia minora fuse due to low estrogen, irritation, or scarring.
- Seen in: Postmenopausal women, postpartum, or chronic irritation.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Adjunct to hormonal or surgical treatment — scar softening, touch reintroduction.
20. Neurogenic Sexual Dysfunction
Sexual dysfunction caused by nerve damage or neurological conditions.
- Examples: Multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, diabetic neuropathy.
- Yoni Therapy Role: Sensory reawakening, modified touch therapy, and co-treatment with neurophysiologists.
Conclusion: A Holistic View
Female sexual disorders are real, diverse, and treatable. While medical diagnosis is essential, somatic therapies like yoni therapy offer embodied healing for pain, numbness, or emotional disconnection. Healing happens when physiology, psychology, and touch-based re-integration come together.
Always consult with your doctor or a certified pelvic floor therapist before beginning any internal work.
Note to Practitioners: This guide references ICD-11 and DSM-5 classifications, and is aligned with trauma-informed and consent-based bodywork practices.

 Tags:
Tags: